Overview
Affinidi Messaging is a communication system built on the DIDComm v2.1 protocol. It ensures complete privacy and control of user data and identity during interactions with individuals, businesses, and AI agents.
What is DIDComm
The DIDComm v2.1 protocol is an open standard for decentralised communication. It is built on Decentralised Identifiers (DIDs), which allow parties to exchange verifiable data such as credentials and establish secure communication channels without relying on centralised servers.
DIDComm works seamlessly with the Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) model. It acts as the communication layer that gives users full control over their privacy and identity during digital interactions.
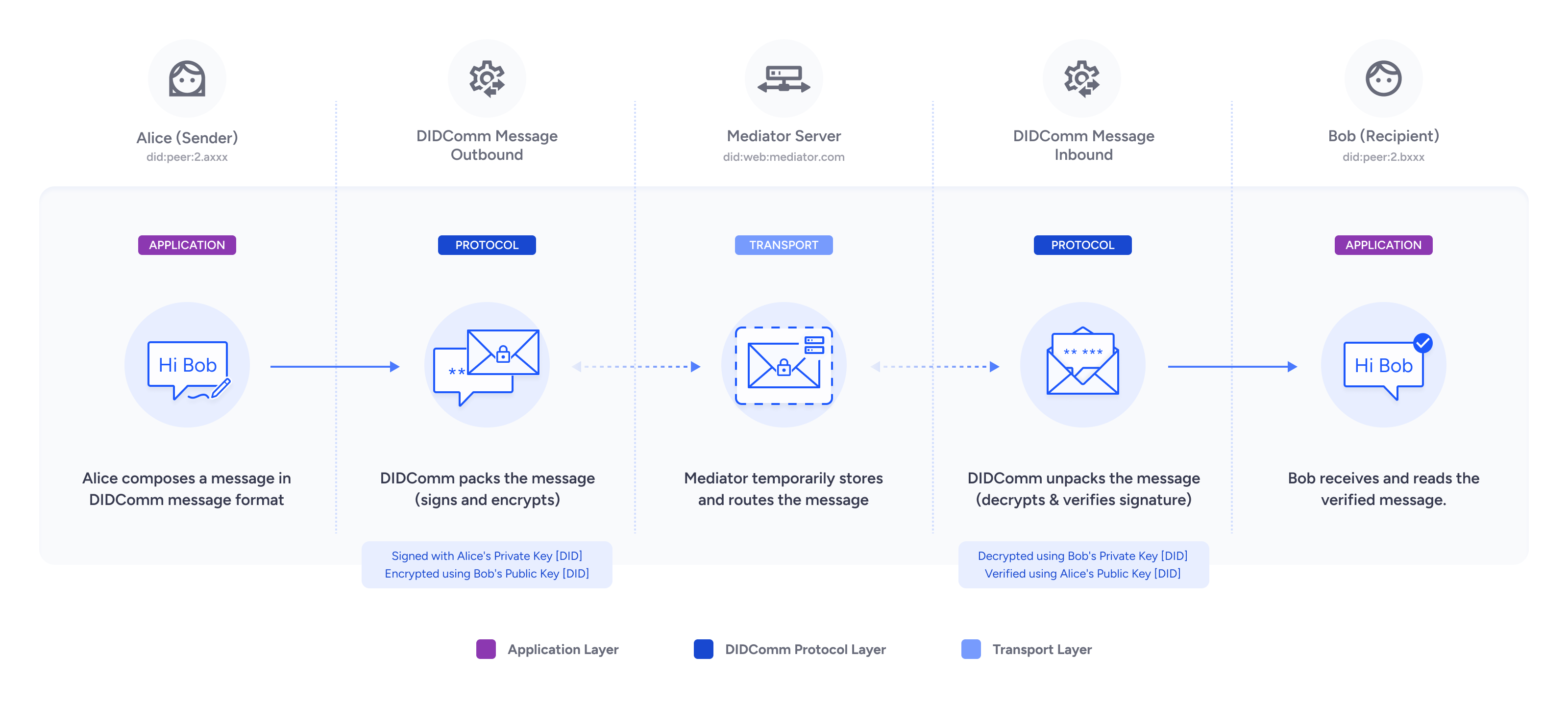
DIDComm v2.1 unlocks several key capabilities for secure, decentralised communication:
Verifiable Credential Exchange: Supports trusted issuance, transmission, and verification of digital credentials between holders and verifiers. This ensures data integrity and authenticity.
Encrypted AI Agent Communication: Enables confidential, end-to-end encrypted messaging between AI agents across different environments and transport layers.
Decentralised API Layer: Provides a secure, message-based alternative to traditional REST APIs. It offers strong message-level encryption that goes beyond standard transport-layer security.
Why use DIDComm
Trusted Digital Interaction: DIDComm uses DIDs to sign and verify message authenticity. Both parties can authenticate each other, reducing fraud risks, especially when interacting with businesses or AI agents.
Privacy by Design: Messages are sent with end-to-end encryption by default, minimising metadata exposure. This ensures that only the intended recipient can access the message content, while the messaging server or mediator has no visibility into it.
End-to-end Encryption: Messages are encrypted using public key cryptography. The recipient’s public key, published via DID, ensures only the intended recipient can decrypt the content.
Interoperable and Transport-Agnostic: DIDComm works across devices and channels, including HTTP, WebSockets, and Bluetooth. It does not rely on transport security for trusted communication.
Flexible Implementation: DIDComm is modular and extensible. It supports diverse use cases, including RESTful APIs, and integrates with open standards like OID4VCI and OID4VP for credential exchange.
Key components
Decentralised Identifier (DID)
A DID is a globally unique identifier that enables secure interactions. It is central to Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI), which gives individuals control over their digital identity.

DID resolution produces a DID Document that containing public key details for encryption and verification, as well as service endpoints for authentication and messaging.
DIDComm Message
A JSON Web Message (JWM) is a lightweight, secure, and standardised format for structured communication using JSON. It includes headers, message types, routing metadata, and payloads designed to enable secure and interoperable communication across different systems.
Message format
The DIDComm message format defines how messages are structured for secure, interoperable communication between parties within a decentralised ecosystem.
{
id: "9c8dcdc3-b41c-46ed-8bae-9dd3ce016568",
typ: "application/didcomm-plain+json",
type_: "https://affinidi.com/didcomm/protocols/1.0/data-response",
body: {
"response_requested": true,
},
from: "did:peer:2.VzDnaecahsBv8WxteYAUfn8cSzZmZ5DKhtfLT1uKW52MpNzauu...",
to: [
"did:web:mediator.example.com",
],
thid: None,
pthid: None,
extra_headers: {},
created_time: 1761540161,
expires_time: 1761540461,
from_prior: None,
attachments: [],
}Key properties of the DIDComm Message:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| id | A unique message ID across all messages in the mediator. |
| type_ | A URI or a string that references a message schema or protocol definition. It helps agents understand how to process the message. |
| to | An array list of DIDs of the recipients. |
| from | The DID of the sender. |
| thid / pthid | Threading fields for message context (e.g. replies, conversations). |
| expires_time | The message expiry time used by the sender when they will consider the message as “expired”. |
| attachments | Contains external content within a message, such as documents, credentials, images, or other data, without embedding them directly in the message body. |
For more details about the structure of DIDComm Message, refer to the Plaintext Message Structure section of the DIDComm v2.1 specification.
DIDComm Envelopes
DIDComm messages can be composed into different formats, plaintext, signed, and encrypted. Within the DIDComm protocol, these formats are referred to as envelopes.
Combining DIDComm Envelopes
DIDComm supports combining multiple message formats to deliver robust security benefits across decentralised communication channels:
Confidentiality: Ensures that only intended recipients can read the message content. Mediators and intermediaries cannot access its contents.
Sender Authenticity: Allows recipients to verify the identity of the sender, ensuring the message originates from a trusted source.
Non-repudiation: Prevents the sender from denying that they sent the message, thanks to cryptographic signing.
Sender Anonymity: Protects the sender’s identity from being exposed to mediators or intermediaries during message routing.
Refer to the table representation of the security benefits when combining different envelopes.
Combine envelope types to meet specific security goals across confidentiality, authenticity, and privacy. For more details about envelopes, refer to the IANA Media Types section of the DIDComm v2.1 specification.
Mediator (Agents)
A mediator is a messaging server that routes messages securely between parties, such as individuals, businesses, or AI agents. Mediators cannot access message content.
Mediators provide capabilities such as:
Message Routing: Mediators handle encrypted forward messages and pass them on to the intended recipient. The message remains fully end-to-end encrypted, ensuring that the mediator cannot access or read its contents.
Message Storage & Pickup: Temporarily store messages and enable asynchronous communication.
A DIDComm mediator works like a decentralised SMTP relay, ensuring privacy, integrity, and independence from transport protocols.